Notice: As part of our surveillance and to reduce risk of infection, we have updated our patient and visitor policy. Click here for more information
Type 1 Diabetes
Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes refers to a variety of Diabetes where there is an almost total lack of Insulin production by the patient.
Insulin is an essential hormone that allows your body’s cells to use glucose for energy by passing the glucose from your blood to your body’s cells. When your tissue has enough glucose, the extras glucose is stored into glycogen. During periods of activity or exercise, glycogen is transformed into glucose for energy.
Individuals diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes are unable to process glucose due to a lack of insulin. Therefore, causing high blood sugar levels that lead to a series of problems. The Patient is thus totally insulin dependent to sustain life. Note that the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is that type 1 is the result of the body not producing insulin, however, type 2 is the result of the body not responding effectively to insuli
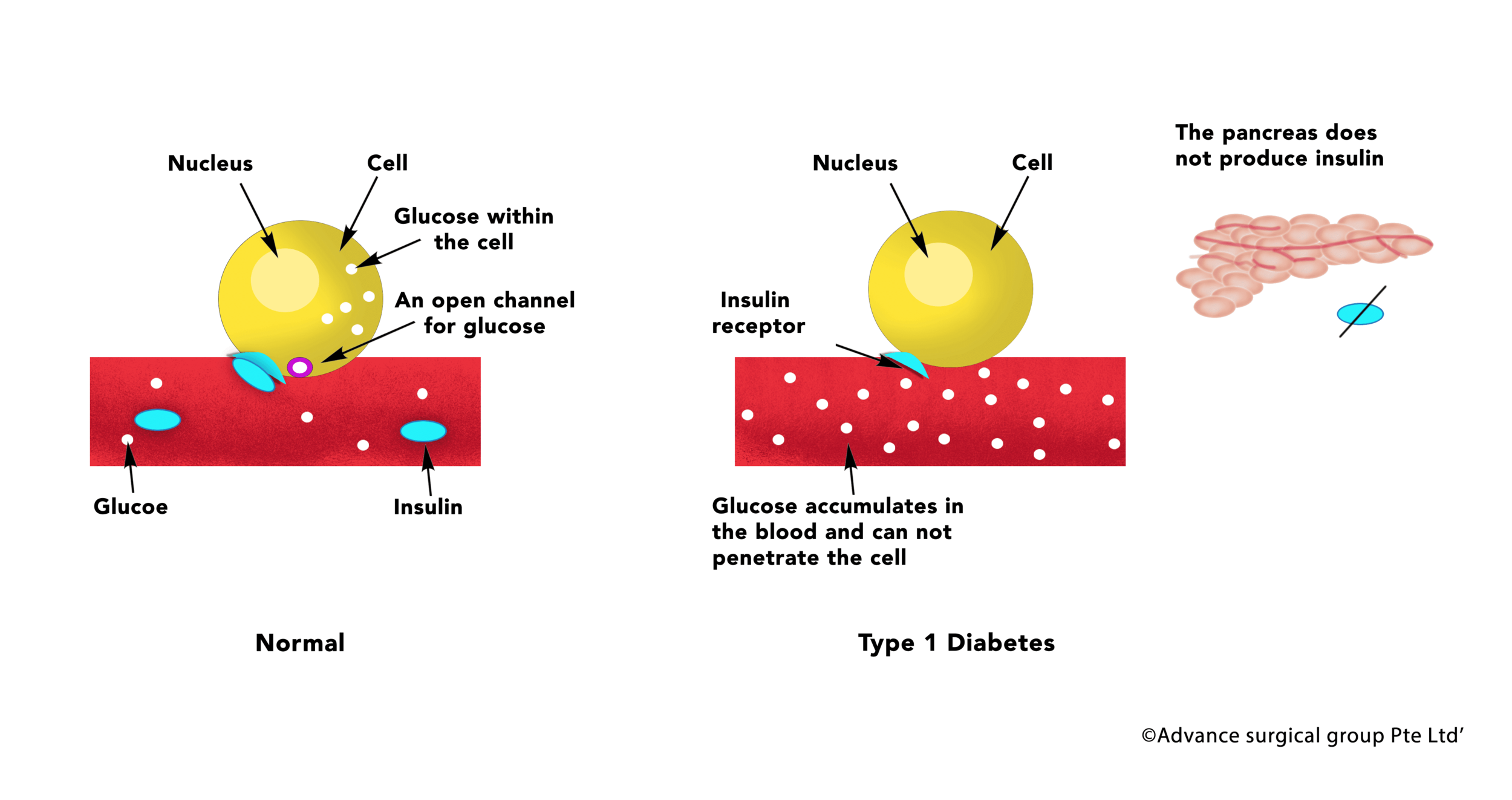
How common is Type 1 Diabetes in Singapore?
The prevalence of Diabetes in Singapore is about 13.7 %. About 5% of Diabetics have Type 1 Diabetes. The incidence of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are increasing rapidly.
What causes Type 1 Diabetes?
It is largely thought that the cause is an autoimmune disease. However, the exact cause and mechanism is not fully understood. The patient’s own antibodies destroy the cells that produce insulin. Other environmental causes like viruses, toxins and the destruction of the pancreas or islet cells are factors to its cause. Also, could be due to accidents and surgery.
What are the symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes?
Patient’s with Type 1 Diabetes incur many problems without insulin. The most serious being ketoacidosis which is a very serious symptom of diabetes. Symptoms include:
- Vomiting or stomach pain
- Fruity breath odor
- Nausea
- Rapid breathing
Milder symptoms include:
- Excessive Hunger
- Excessive Thirst
- Feeling tired all the time
- Cuts that won’t heal or heal very slowly
- Frequent urination
- Increased weight loss across a short time frame
They also suffer from all the complications of Type 2 Diabetes if they are not well controlled. The disease attacks major and micro blood vessels. leading to organ and tissue damage. Some of the things that could happen are stroke, heart attack, kidney failure, blindness, nerve damage and loss of limbs.
If you are experiencing similar symptoms, please make an appointment with us right away. However, in the case of ketoacidosis, admitting into a hospital emergency may be necessary.
How do we diagnose Type 1 Diabetes?
Fasting blood sugar and HbA1c are the initial tests. (HbA1c test measures the average blood sugar level across 3 months) To look for the cause, anti islet cell and anti GAD antibodies can be done. What does this tell us? A C peptide will document endogenous insulin production. Other tests are directed at assessing end organ damage. An eye examination for retinopathy for instance would also be a strong indicator.
Individuals are diagnosed if they meet one or more of the following criteria:
- fasting blood sugar > 126 mg/dL on two separate tests
- random blood sugar > 200 mg/dL, along with symptoms of diabetes
- hemoglobin A1c > 6.5 on two separate tests
There are cases where Type 1 Diabetes is misdiagnosed with having type 2 due to the similarities in symptoms, however, this is quickly rectified during the treatment process of the disease.
Risk factors that aid the diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes are
- You have a family history of diabetes
- High risk ethnicity (Asian Indians, Filipino and Native Hawaiian/ Pacific Islander and others)
- Do not regularly do physical activity
What is the treatment options for Type 1 Diabetes?
The life-saving treatment is insulin. It keeps the patient alive but does not reverse or cure the disease.
Best management practices involve an insulin pump and a continuous sugar monitor. This allows the most accurate way to monitor and control the blood sugar within a chosen range.
Total reversal of the condition requires islet cell transplant or whole pancreas transplant. Both are very expensive and introduces new problems as they require immunosuppression with attendant continuing cost and complications.
Metabolic surgery does not work for Type 1 Diabetes as it works for Type 2. Obese patients with Type 1 Diabetes do benefit from bariatric surgery as it makes the Diabetes easier to control by reducing insulin resistance. Less insulin is then needed leading to costs savings.
Stem cell research hold promise of an eventual cure.
The artificial pancreas is also another promising technology but is not widely available and is likely expensive.
In terms of lifestyle, creating an eating plan to manage glucose intake and regular exercise will allow long term diabetes management.
If you are interested in knowing more about treatment and management of Type 1 Diabetes, please arrange an appointment with one of our medical professionals.
How is Type 1 Diabetes controlled?
Strict blood sugar monitoring coupled with accurate insulin management remains the mainstay of management. A continuous sugar monitoring device which allows one to check blood sugar on a smart phone through an app is a very effective means to regulate blood sugar. In comparison to the more conventional way of pricking multiple times daily.
Does diet and lifestyle matter?
Very much so. Type 1 diabetics should exercise regularly, have a low carb, low sugar diet and keep slim. Continuous sugar monitoring will help the patient see the effects of various foods and activity on the blood sugar.
What are the signs of trouble for Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetics should have regular screening for damage to end organs like heart, kidney, brain, eyes and feet. It’s better to pick up complications early so that they can be managed.
If blood sugar levels go very high, the most feared complication is diabetic ketoacidosis which leads to coma and possibly death if gone un-treated.
What are the risks of untreated Diabetes Type 1?
Untreated type 1 Diabetes can lead to several problems, the most serious being Ketoacidosis which can cause death. Other issues can arise, such as:
- Shortened life expectancy
- Increases the risk of heart attack and stroke
- Increases the risk of liver, pancreas, colorectal breast and bladder cancer by 20-50%
- Peripheral arterial disease with risk of lower limb amputation. (Damaged arteries)
- Peripheral nerve disease leading to trauma, sepsis and increased risk of amputation (Damaged nerves)
- Kidney disease from diabetic nephropathy leading to kidney failure and dialysis
- Delayed wound healing due to damage to small arteries
- Increased susceptibility to infection including Covid. Increased chance of morbidity and mortality from Covid
- Diabetic retinopathy leading to blindness due to small vessel damage to the retina
- Skin diseases which include blisters, open sores, yellow, reddish or brown patches.
- Sexual dysfunction in men and women due to arterial and nerve damage
- Autonomic neuropathy leading to host of symptoms
How do I prepare for an appointment with ASG?
Most appointments concerning Type 1 Diabetes would require blood testing. It would be good to come on an empty stomach so that fasting blood test values may be checked. If you are experiencing symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes, please make an appointment with us.
Make an appointment with us today.
Kindly fill out the form below with your details.
Disclaimer: By submitting, you agree to ASG’s terms and conditions.. Please note that your information will be handled confidentially.

